- Shanghai Zhongshen International Trade Co., Ltd. - Two decades of trade agency expertise.
- Service Hotline: 139 1787 2118
——Practical Guide by a 20 - year Senior Practitioner
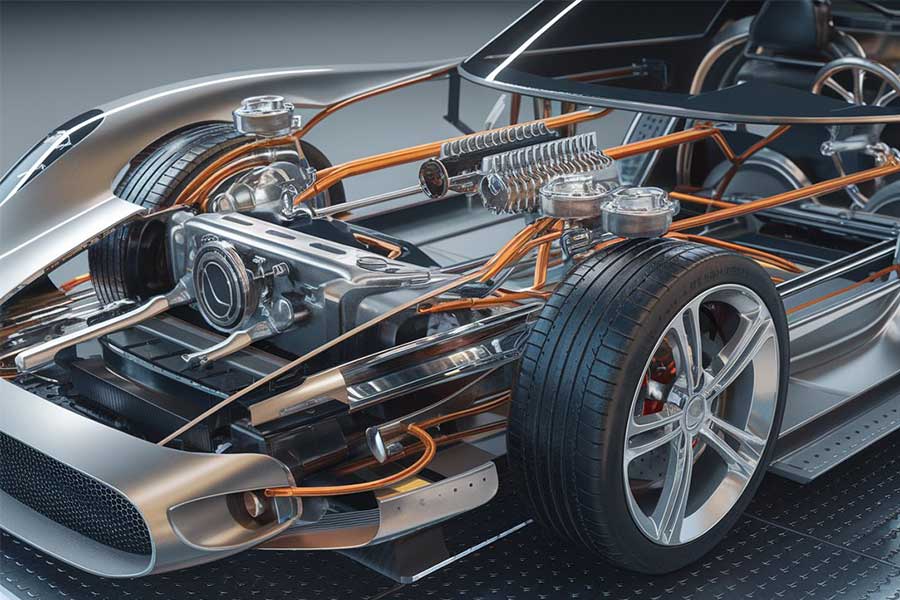
Against the backdrop of the booming development of the global automotive industry, rail transit, and machinery manufacturing fields, as a key component, the import demand for shock absorbers continues to grow. However, due to the complex product technical standards, strict customs supervision, and long supply chain cycle, the shock absorber import business has a high degree of dependence on professional agency services. As a practitioner with 20 years of agency experience, this article will deeply analyze the core points of shock absorber imports and provide practical suggestions for enterprises to avoid risks and improve efficiency.foreign tradeI. Market Status and Product Classification of Shock Absorber Imports
Global Supply Chain Pattern
1.The high - end market is dominated by Germany (Sachs, Bilstein) and Japan (KYB, Tokico), and emerging production bases in Central and Eastern Europe and Southeast Asia are rising
- The import volume of vehicle - specific shock absorbers has increased by 27% year - on - year, and lightweight and intelligent technologies have become the core procurement standards
- In 2023New energyProduct Technical Classification
2.Three technical routes of hydraulic / pneumatic / electromagnetic (special attention should be paid to the differences in HS code classification)
- For automotive suspension systems (including OE supporting parts / aftermarket replacement parts), special - purpose for industrial equipment (high - temperature resistant / corrosion - resistant)
- II. Key Points of Full - Process Risk Management for Shock Absorber Imports
Stage 1: Supplier Qualification Review
It is necessary to verify whether the factory holds IATF 16949 certification and product EC certification (such as EU ECE R105 standard)
- Case: A company failed to verify the validity of the E - mark certificate of a Turkish supplier, resulting in the destruction of a full container of goods at the Port of Rotterdam
- Stage 2: Trade Term Negotiation
Under the CIF clause, requirements for documents accompanying the goods such as vibration test reports and salt spray test data shall be clearly defined
- Under CIF terms, requirements for accompanying documents such as vibration test reports and salt spray test data must be specified
- In DDP operations, pay attention to the anti - dumping duty risks in the destination country (for example, India levies an additional 14% duty on some hydraulic shock absorbers).
Phase 3: Declaration and Customs Clearance
- Key declaration elements:
- Material composition (the classification is affected by whether the main body is made of aluminum alloy or steel)
- Applicable vehicle types (there are tariff differences between commercial vehicles and passenger cars)
- Pressure value range (involving the supervision of special equipment)
- Typical Case: A batch of electromagnetic shock absorbers was declared as "Automotive parts"The technical parameters were not reflected, triggering customs classification inquiries and resulting in a 35-day port detention."
Phase 4: Logistics and Warehousing
- Shock - proof packaging must comply with the ISTA 3E transportation test standard to avoid performance damage caused by long - distance transportation.Maritime TransportationPerformance damage caused by long - distance transportation.
- Temperature-controlled warehouse storage requirements (rubber components are prone to aging in environments with humidity >70%).
III. Solution Library for Industry Pain Points
1.Breakthrough of technical barriers.
- The latest EU Regulation (EU) 2023/154 puts forward new requirements for the environmental friendliness of damping media.
- Coping strategy: Entrust SGS in advance to conduct REACH regulation compliance verification.
2.Cost optimization path
- Utilize the RCEP agreement to implement tariff concessions on shock absorbers produced in ASEAN (products from Philippine factories can have their tariffs reduced to 3.5%).
- Establish a "Bonded Testing and Maintenance Center" to reduce the cost of returning after-sales parts.
3.Construction of supply chain resilience
- It is recommended that the customer implement a "dual-origin procurement" strategy (such as a combination of European and Mexican factories).
- Enterprises certified by AEO can enjoy the customs clearance convenience of a 70% reduction in the inspection rate.
Market Size and Category Characteristics
1.Market Early Warning
- The United States intends to include smart shock absorbers in the scope of ECRA export control (involving military - grade damping control algorithms).
- Certification challenges brought about by the rise of the African market (for example, Nigerias SONCAP has added dynamic load testing).
2.Digital transformation
- Use blockchain technology to trace the authenticity of damping coefficient test reports.
- Establish a supplier production capacity database to monitor in real - time the production risks of factories in earthquake - prone areas in Japan and South Korea.
3.service model innovation
- "Technical Compliance Hosting" Service: Covers EU ELV Directive and China GB/T 19548 Standard Update Tracking
- Supply chain finance solution: Provide inventory pledge financing for small and medium - sized importers based on import data.
Conclusion
The import business of shock absorbers has shifted from simple trade execution to in-depth service competition, such as technical compliance management and supply chain resilience building. Professional agencies need to establish a composite service team consisting of "technical experts + legal advisors + logistics engineers" to help enterprises navigate the complex international trade environment. It is recommended that importers focus on the new amendments to the EU Machinery Regulations to be implemented in 2024 (involving upgrades to fatigue testing standards for shock absorbers) and proactively plan technical rectification solutions.
(Data sources of this article: General Administration of Customs of China, US Department of Commerce, TUV Rheinland test report of Germany)
Related Recommendations
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. Shanghai ICP No. 2023007705-2  PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912
PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912